Energy Performance Ratings: What You Need to Know
One of the many factors that homeowners consider when purchasing new windows is the energy performance rating. This rating system tells homeowners how much heat and light can be transmitted through a window. The energy performance rating also shows how much air leaks through windows.
This information is important because it can have a big effect on the energy efficiency of the window. Knowing the energy performance rating can help homeowners determine how they can expect their home's utility bills to change when they install new windows.
Here are the factors every homeowner should know and what we will cover:
- What Are Energy Performance Ratings?
- Why Are Ratings Important?
- Where Can I Find Performance Ratings?
- What Do Energy Performance Scores Mean?
- What Are the Best Scores?
What Are Energy Performance Ratings?
Energy performance ratings are the measurement of a window's energy efficiency. Energy performance measurements are determined by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC), an organization that tests and certifies windows, doors and skylights based on energy performance ratings. Rated windows are labeled to make it easy for consumers to compare products.
Every ENERGY STAR qualified window has an NFRC label. The ENERGY STAR certification comes from the SHGC (solar heat gain coefficient) and U-factor. Other energy performance measurements include visible light transmittance and air leakage, both of which are found on the NFRC window labels (1, 2).
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
Solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) is the amount of solar heat that reaches the window compared the amount of heat that gets inside. Less solar heat gain is especially effective when temperatures are warm outside. In cold winter months, a lower U-factor is especially important (3).
It's worth noting that for some windows, like windows that face west and south, the contractor may recommend a higher or lower SHGC than in the rest of the house, because the amount of solar energy that reaches this window will be higher than in other parts of the house.
Higher SHGC values usually come with higher U-factors, which can impact a home's energy efficiency.
U-Factor
U-factor is the rate of heat loss in a window assembly. Resistance to heat flow is what makes a window insulated. In this case, higher resistance equals better insulation. When the U-factor is measured, the whole window, including the glazing, spacers and frame are all taken into consideration. More insulation produces a lower U-factor number.
Some window U-factor performance numbers are as low as 0.15 (the most energy efficient windows will usually have a U-factor between 0.30 and 0.15. More on this below) (4).
Visible Transmittance
Visible transmittance is a value that indicates the amount of visible light that makes it through the window. At one time, the amount of light that was able to penetrate the window and the amount of solar heat gain was the same (5).
Now with low-e coatings and other break-through technologies, a window can have high visible transmittance with a low solar heat gain. This ensures that the room gets light without becoming hot and uncomfortable.
Light to solar gain is measured by creating a ratio between the solar heat gain coefficient and the visible transmittance. Higher ratios indicate that a lot of visible light is transmitted through the window. This rating isn't always provided.
Air Leakage
Air leakage is the amount of air allowed to leak through the window's frame. Air leakage can change over time, as materials expand and contract and as some materials become warped (6).
Air leakage is very difficult to measure, so it's important to remember that this number on the energy performance rating label is an estimate only.
Why Are Ratings Important?
Energy performance ratings on windows are important because they can help the homeowner gauge his or her expected energy savings if they decide to install new windows. Ratings also help homeowners compare one window to another as they try to decide which window is right for them.
Where Can I Find Performance Ratings?
Energy performance ratings can be found on the window label, often found in the lower right-hand corner of the window. The label has all four types of ratings on one sticker (7, 8).
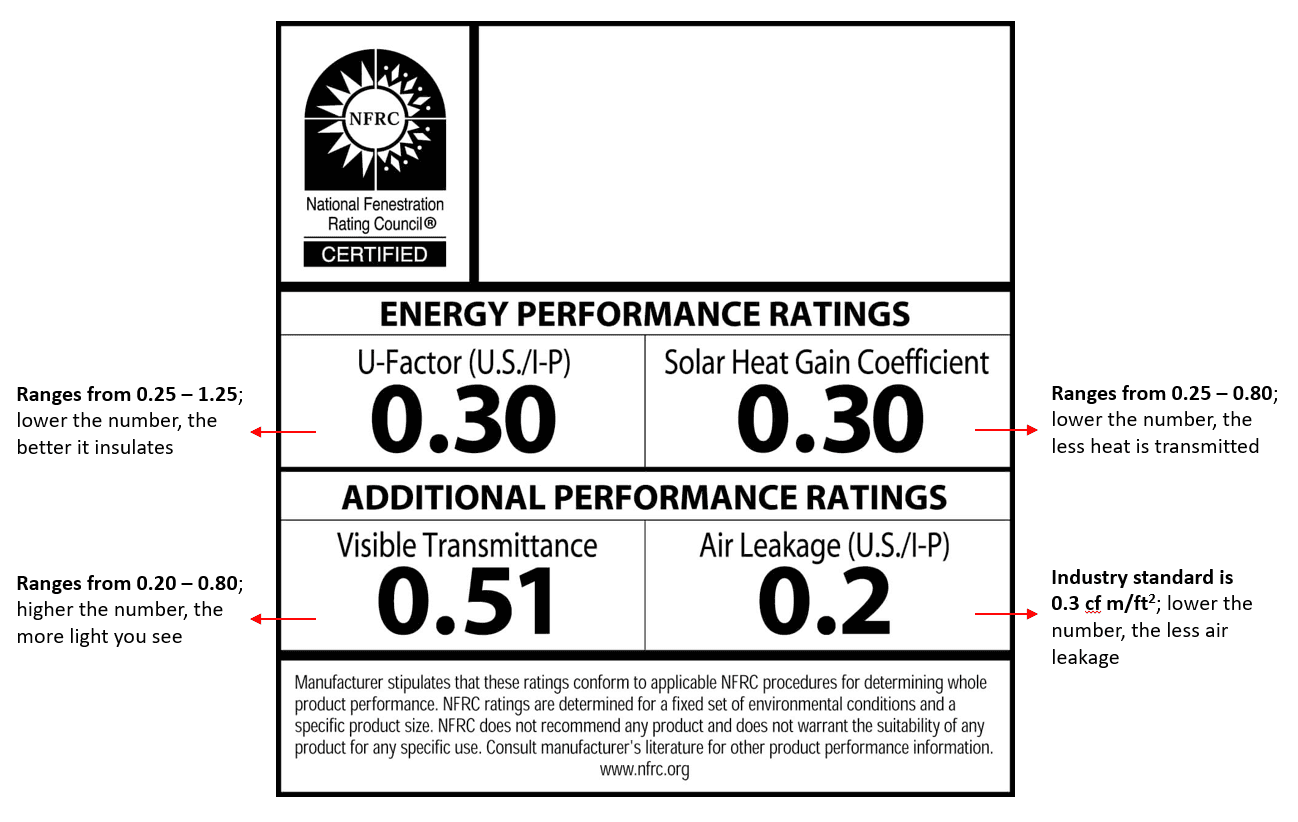
What Do Energy Performance Scores Mean?
In general, energy performance ratings convey the relative energy efficiency of a window. To homeowners who are concerned with saving money and reducing their energy bills, the energy performance scores can mean lower utility bills and less energy wasted (9).
The best way to ensure that the windows you buy are best for your needs is to work with a window contractor. Your window expert can work within your budget to recommend windows that will be energy efficient.
What Are the Best Scores?
To the average homeowner, performance scores can seem like meaningless numbers. Knowing the meaning of these numbers can help you decide which window is right for you (10, 11).
U-Factor Ratings
The best U-factor ratings for a cold climate falls between 0.15 and 0.39. The low end of the range can only be achieved with triple-glazed windows. In a hot climate, the best U-factor ratings fall between 0.17 and 0.30. To put this in perspective, a standard clear window with one pane of glass will have a U-factor rating of approximately 1.09. In general, look for the lowest U-factor when buying energy efficient windows.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient Ratings
The best solar heat gain coefficient rating can sometimes depend on the location of the walls and the type of climate where the home is located. Higher solar heat gain numbers may be okay in cold climates on south-facing walls. In hot climates, values as low as 0.25 are considered good. The solar heat gain coefficient for a standard piece of clear glass is approximately 0.81. The safest approach when deciding on replacement windows would be to go for both a low U-factor and a low solar heat gain coefficient. This will allow for the best performance all year long.
Visible Transmittance Ratings
Visible transmittance ratings fall between 0 and 1, with higher numbers corresponding to more light transmittance. Typically, homeowners want a higher number for more light, but sometimes homeowners seek to cut back glare to make a room more comfortable.
Homeowners who cut back too much on visible transmittance may find themselves using artificial light even during the day time. In addition, house plants can die without enough light.
Air Leakage Rating
Air leakage rating runs between 0.1 and 0.3, and lower numbers are better. The more air that leaks out of a window, the less energy efficient the window is.
